Your Diet for
Metabolic Therapy
The metabolic approach to cancer treatment focuses on altering the body’s metabolism to create an environment that is less conducive to cancer cell growth. Diet plays a crucial role in this approach, as it can significantly impact the body’s metabolic state.
The Process
The First Step
Principles of a Metabolic Diet
Your diet is a cornerstone of metabolic therapy, designed to create an environment that is less favourable for cancer cell growth. By strategically altering the body’s metabolism, this diet aims to deprive cancer cells of their primary fuel sources while supporting overall health and well-being. The principles of a metabolic diet focuses on calorie restriction, ketogenic nutrition, and intermittent fasting, all of which play a crucial role in enhancing the body’s metabolic flexibility and reducing cancer cell proliferation.
Calorie Restriction
Reducing calorie intake can helps starve cancer cells of one of their primary fuel sources, glucose.
Ketogenic Diet
Switch the body's primary fuel source from glucose to ketones, which cancer cells cannot efficiently use.
Intermittent Fasting
Enhance the body's metabolic flexibility and reduce cancer cell growth.
Calorie Restriction
Half the Battle
Getting your Glucose Ketone Index (GKI) level below 2 (deep ketosis) is the first milestone in effectively utilising the Press/Pulse protocol for combatting cancer. Decreasing glucose and increasing ketones is the goal for your diet.
Reduce Your Calories
For most people, 1500 calories a day is sufficient to sustain your basal metabolic rate (BMR).
Remove Sugar
All forms of sugar will act as a fuel source for cancer cells. Sugar is not necessary in your diet.
Remove Carbohydrates
Your body will convert carbs into glucose. Limit your carb intake to a maximum 20 grams per day.
Ketogenic Diet
Achieving Ketosis
Your body is perfectly happy using ketones as an energy source instead of glucose. Cancer cells are fermenters and require glucose or glutamine because using ketones requires utilising a process called oxidative phosphorylation. Since cancer cells have damaged mitochondria, they cannot use oxygen and ketones as a fuel source.
Add High Quality Fat
Healthy fats are an essential part of a ketogenic diet. Animal fats such as beef fat / tallow, butter and eggs are an excellent source. There are also vegetable which are good sources of healthy fat, though many also contain carbohydrates.
Moderate Protein
You will need to moderate your protein intake to prevent gluconeogenesis (conversion of protein to glucose) while also supporting muscle maintenance.
Nutrient Dense Food
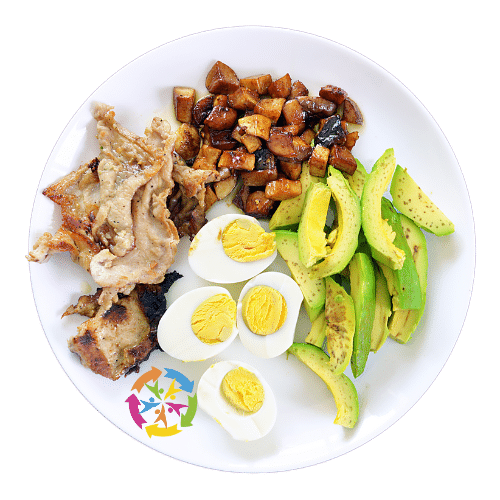
For simplicity, we focus on animal sources for fats and protein since they do not contain sugar or carbohydrates. Beef, pork, lamb, chicken, fish, liver, heart, kidneys, eggs, tallow, lard and butter are all excellent sources of nutrition.
Intermittent Fasting
Kickstart Ketosis
Fasting helps your body reach ketosis more quickly. When you fast, your body shifts its fuel source from carbs to fats, which aligns with the keto diet’s goal. It has been shown to reduce inflammation, which can enhance overall health and complement the anti-inflammatory effects of the keto diet.
Enhanced Fat Burning
Both fasting and a keto diet promote burning fat to produce ketones as the bodies main fuel source. Together they are a powerful combo.
Improved Insulin Sensitivity
Fasting can improve insulin sensitivity, which is beneficial for blood sugar control. This complements the keto diet’s ability to stabilise your blood sugar levels.
Appetite Control
Ketones produced during ketosis can suppress appetite, making it easier to stick to your eating plan and avoid overeating.
Overview
Benefits of a Metabolic Diet
While the main purpose in switching from a standard diet to a ketogenic diet is to effectively utilise the Press/Pulse Protocol, there are a few other beneficial side effects.
Cancer Cell Inhibition
A metabolic diet can inhibit cancer cell growth by depriving them of their primary fuel sources. We’ll discuss how to reduce glutamine levels in the Supplements and ReDO Project sections.
Improved Energy Levels
The potential for improved energy levels and mental clarity due to the body’s adaptation to ketones is exceptional. You may find that removing sugar and carbs from your diet is the best thing your ever did.
Overall Health
Many people find the overall health benefits, including weight management, reduced inflammation, and improved metabolic health to be well worth the effort of switching their diet.
Adopting a metabolic diet as part of your cancer treatment plan can be a powerful strategy to inhibit cancer cell growth and improve overall health. By focusing on calorie restriction, ketogenic nutrition, and intermittent fasting, you can create a metabolic environment that is less conducive to cancer proliferation.
Please remember, the journey to metabolic health is a gradual process, and it’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider before making significant dietary changes. Some “Standard of Care” treatments may not be conducive to a successful metabolic approach.
Embrace the benefits of a metabolic diet and take control of your health journey.


